Index
Precision cleaning
Precision cleaning is a cleaning process that completely removes contaminants and residues from products, as required in industrial manufacturing processes. In the precision cleaning process, even fine particles that cannot be seen with the naked eye are completely removed (fine particle removal), and residues such as ions and oils are removed to a level that does not affect the quality of the product. The precise cleanliness is achieved by optimally combining the physical action of mechanical force and the chemical/physicochemical action. We analyze the components of contaminants and their degree of adhesion in order to determine the cleaning process and cleaning chemicals that can achieve the desired cleaning quality.
Applications
Water-soluble flux removal, Thin film substrates, Printed circuit boards, Flexible circuit boards, Mounting substrates, Electronic components and parts, Lead frames, Precision parts, Image sensors, Semiconductor packages, Power modules, Ceramic packages, Optical lenses, Optical components, Liquid crystal glasses, Photomasks, Plastic lenses, Bonded lenses, Prisms, Eyeglass lenses, Molded plastic products, Automobile parts, Camera parts, Precision metal parts, Precision bearing balls, Cutting parts, Plated parts, Die-cast parts, Precision press parts, Light alloy die-cast parts, Copy drums, etc.
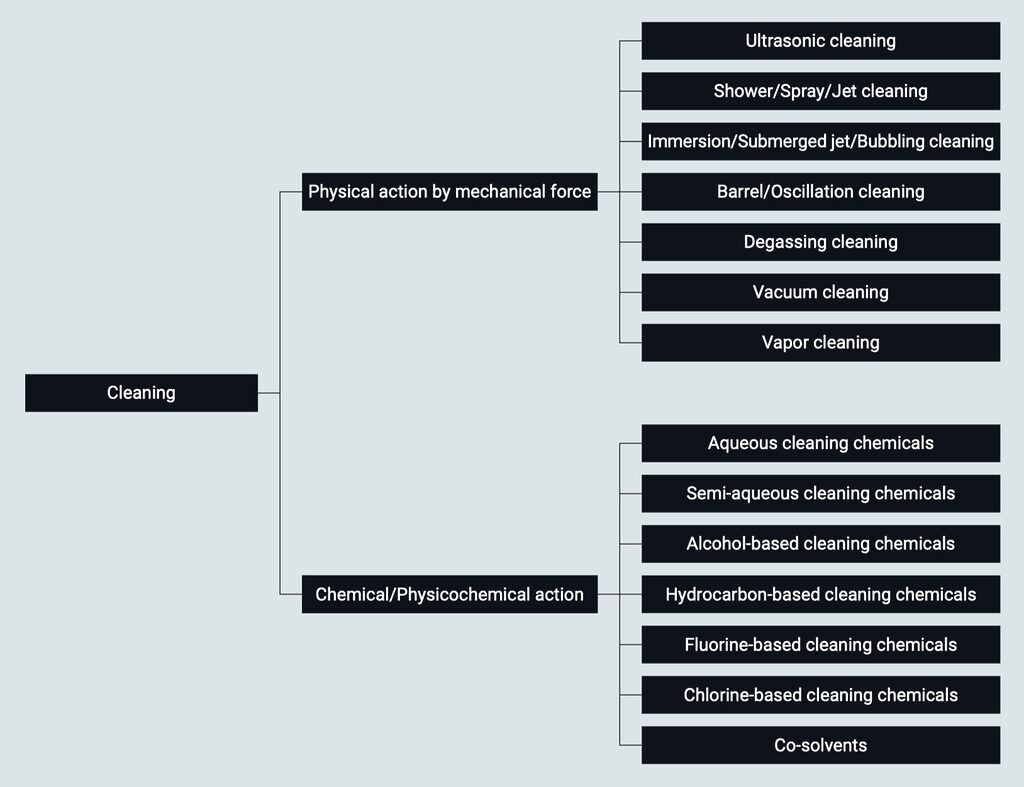
Selection of cleaning processes
When selecting a cleaning process, it is necessary to simultaneously consider the physical action of mechanical force and the chemical and physicochemical action of cleaning chemicals. The optimal cleaning process can be selected from a wide range of options depending on the type, material, and shape of the object to be cleaned, as well as the required cleanliness.



Analysis of contaminants and selection of cleaning chemicals
Selection of cleaning chemicals begins with analyzing the characteristics of the contaminants. The type of contaminants is analyzed to see if it is water-soluble or oil-based, if it contains solids such as particles, and how adhesive the contaminant is, and then a candidate chemical is selected. In addition to the nature of the contaminants, it is necessary to consider the strength and material characteristics of the object to be cleaned. In addition to meeting the required cleaning and drying performance, the cost of the precision cleaning system and the operating costs must be considered together, along with consumption efficiency and the possibility of distillation regeneration. Through partnerships with a wide variety of cleaning chemical suppliers, we rationally determine and propose the most cost-effective chemicals in terms of performance (Click here to learn more about About Precision Cleaning Chemicals).
Selection of cleaning methods
Cleaning methods are considered together with the selection of cleaning chemicals. There is a trade-off between cleaning performance and the strength of the physical action on the object being cleaned. It is necessary to carefully consider the extent to which the strength of the physical action can be tolerated for the physical properties of the object. Cleaning methods also have compatibility with the cleaning chemlcals used, such as whether the blind hole can be cleaned properly, whether excessive foam is generated, etc (Click here to learn more about About Precision Cleaning Systems).


Verification by cleaning trials
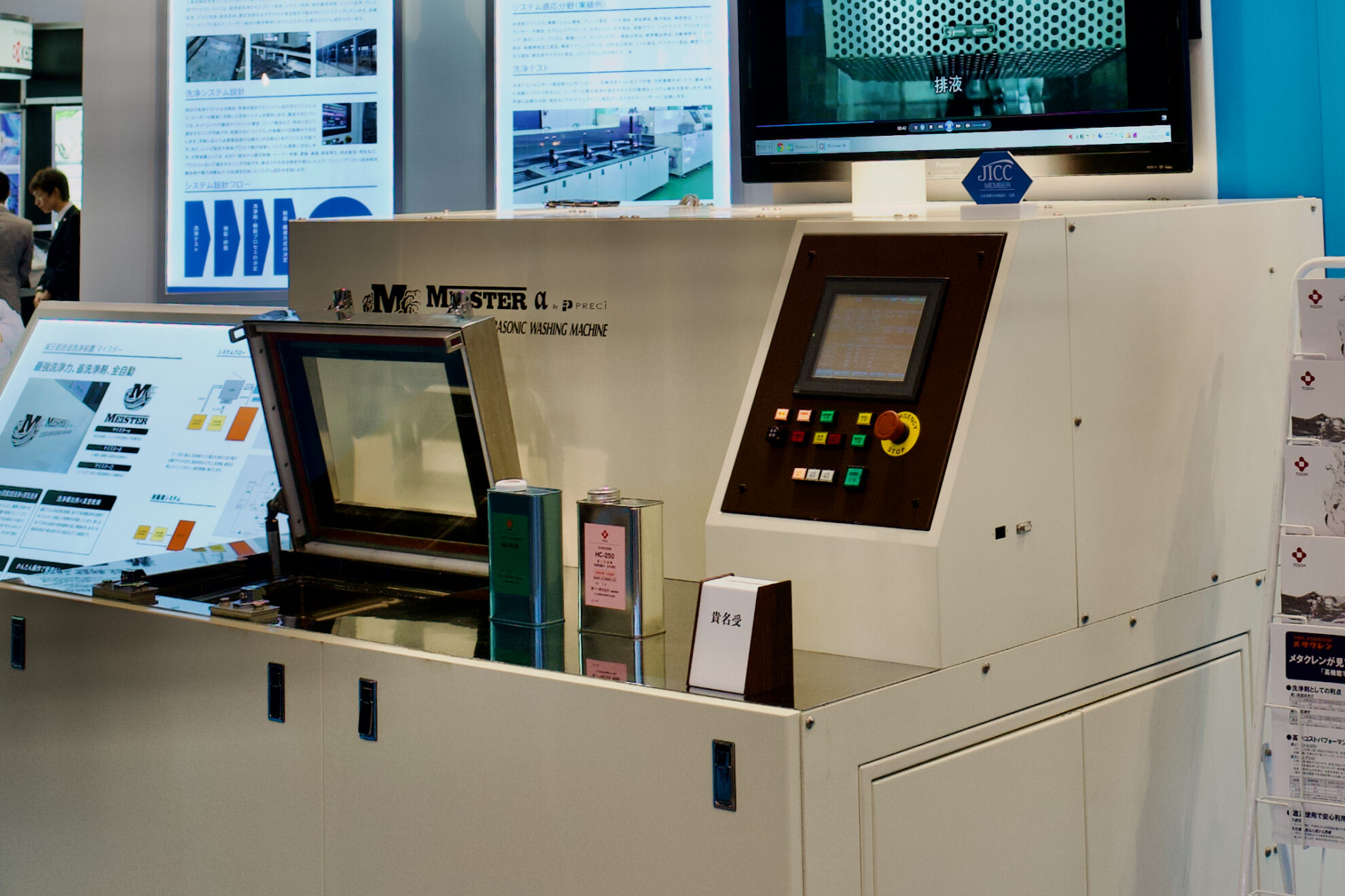
We conduct cleaning trials using actual workpieces at our cleaning test center and determine the cleaning methods and cleaning chemicals based on the on-site evaluation. We comprehensively consider cleaning chemicals, taking into account not only cleaning performance and cost, but also consumption efficiency and the need for additional equipment. We also evaluate the compatibility of the cleaning chemicals and cleaning methods. Based on the verification results, we design a cleaning process that meets the required performance and reduces the total operation cost, including the consumption efficiency of cleaning chemicals and utilities (Click here to learn more about Precision Cleaning Trials & Analytical Measurements).
Process design flow

Process configurations
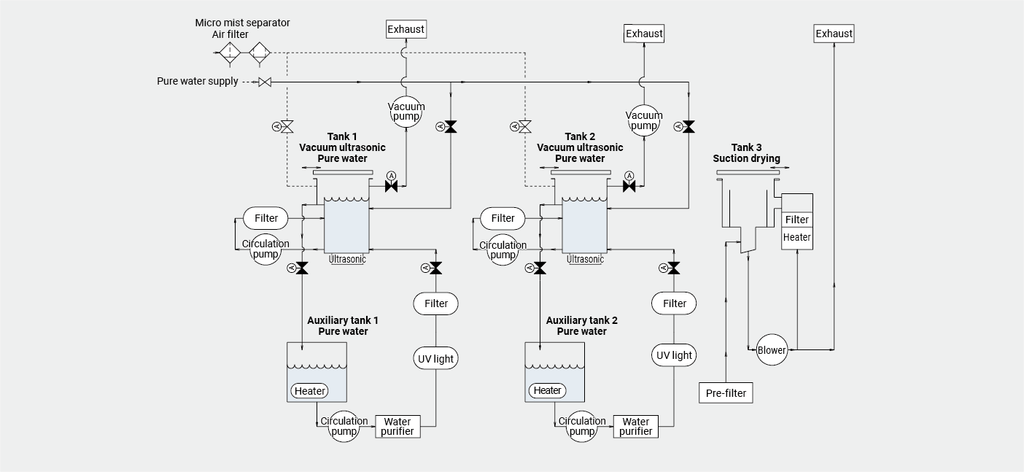
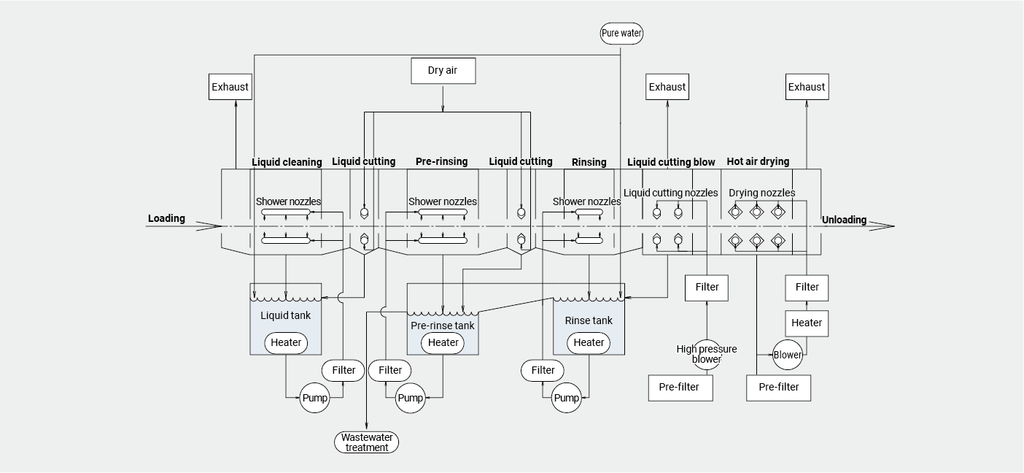
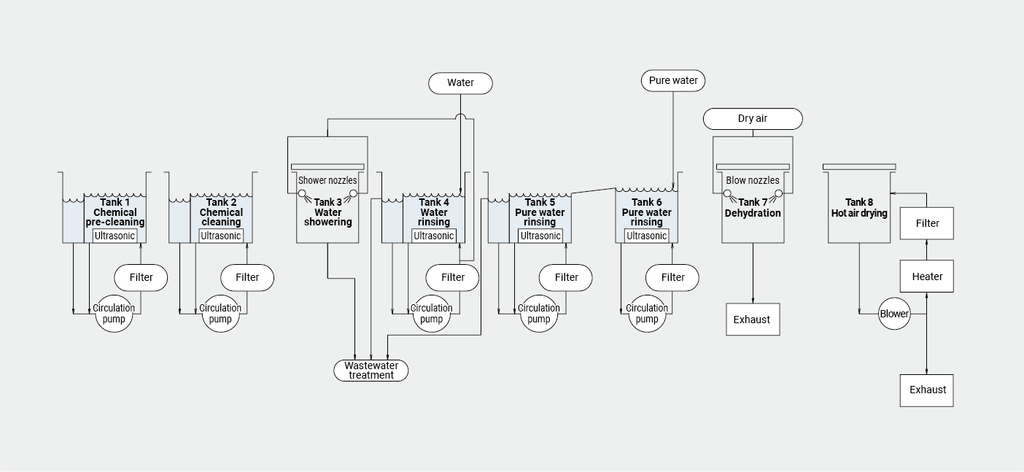
Precision cleaning process generally consists of the following functions:
Cleaning process
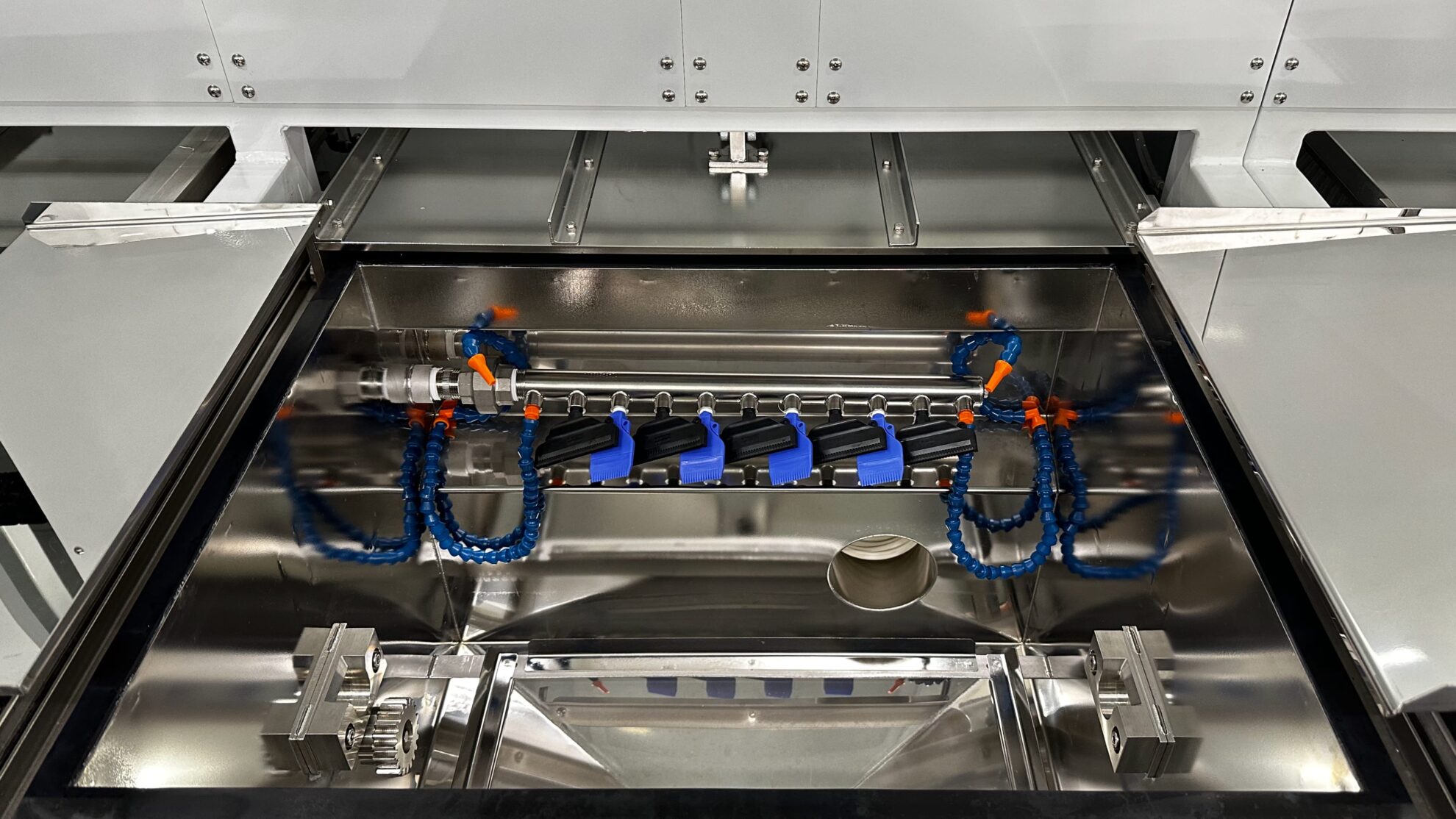
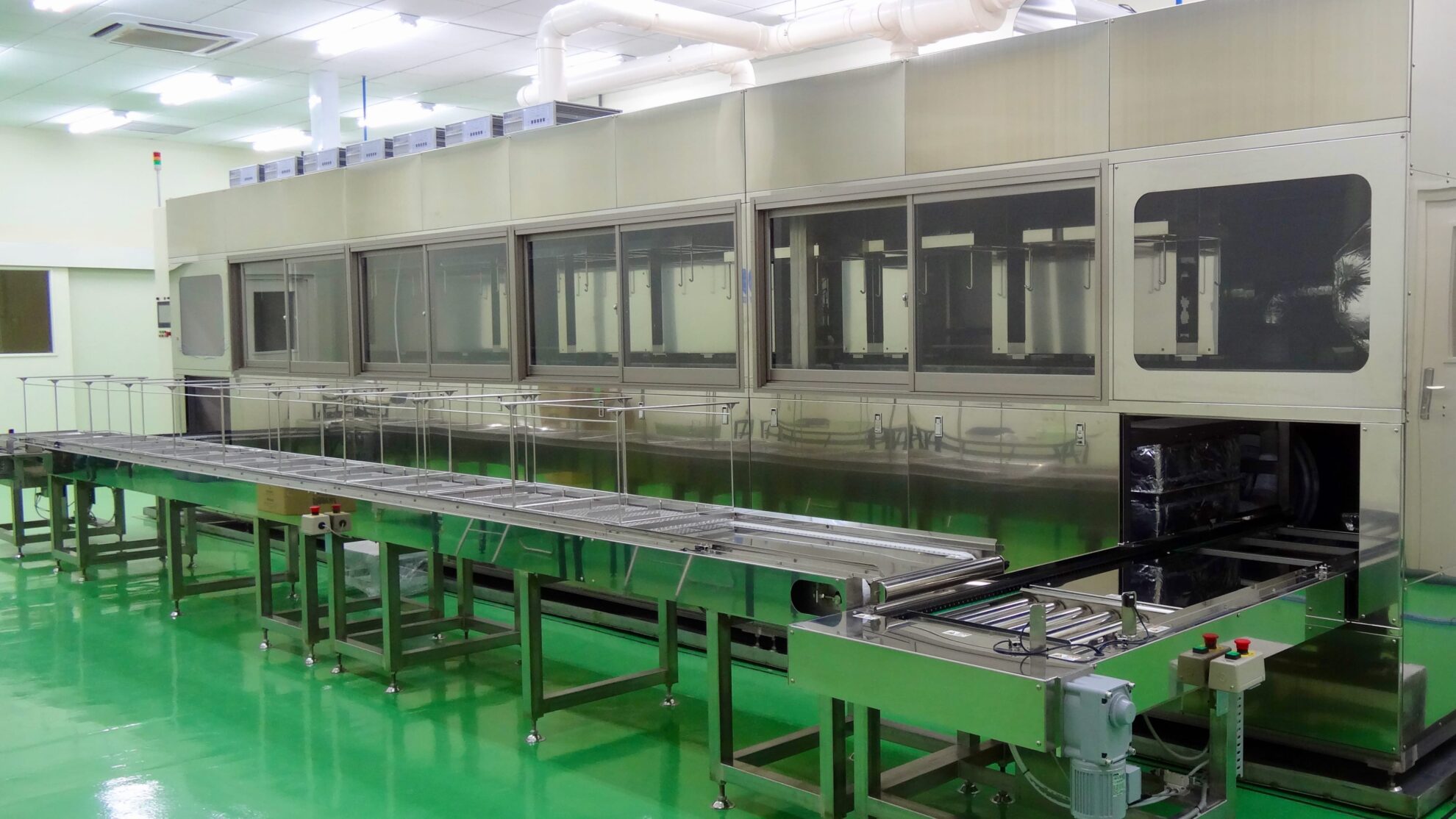
Cleaning with water or liquid chemicals, rinsing, finishing, etc. are performed in the cleaning process. The most suitable cleaning methods are determined from among ultrasonic cleaning, barrel cleaning, vapor cleaning, shower cleaning, etc. The process flow can be continuous, batch, or single wafer.
Drying process
Drying process is carried out after the cleaning process. There are methods for the drying process, such as hot air drying and vacuum drying. Before the drying process, water cutting and dehydration processes or liquid substitution process may be added as necessary.
Ancillary equipment
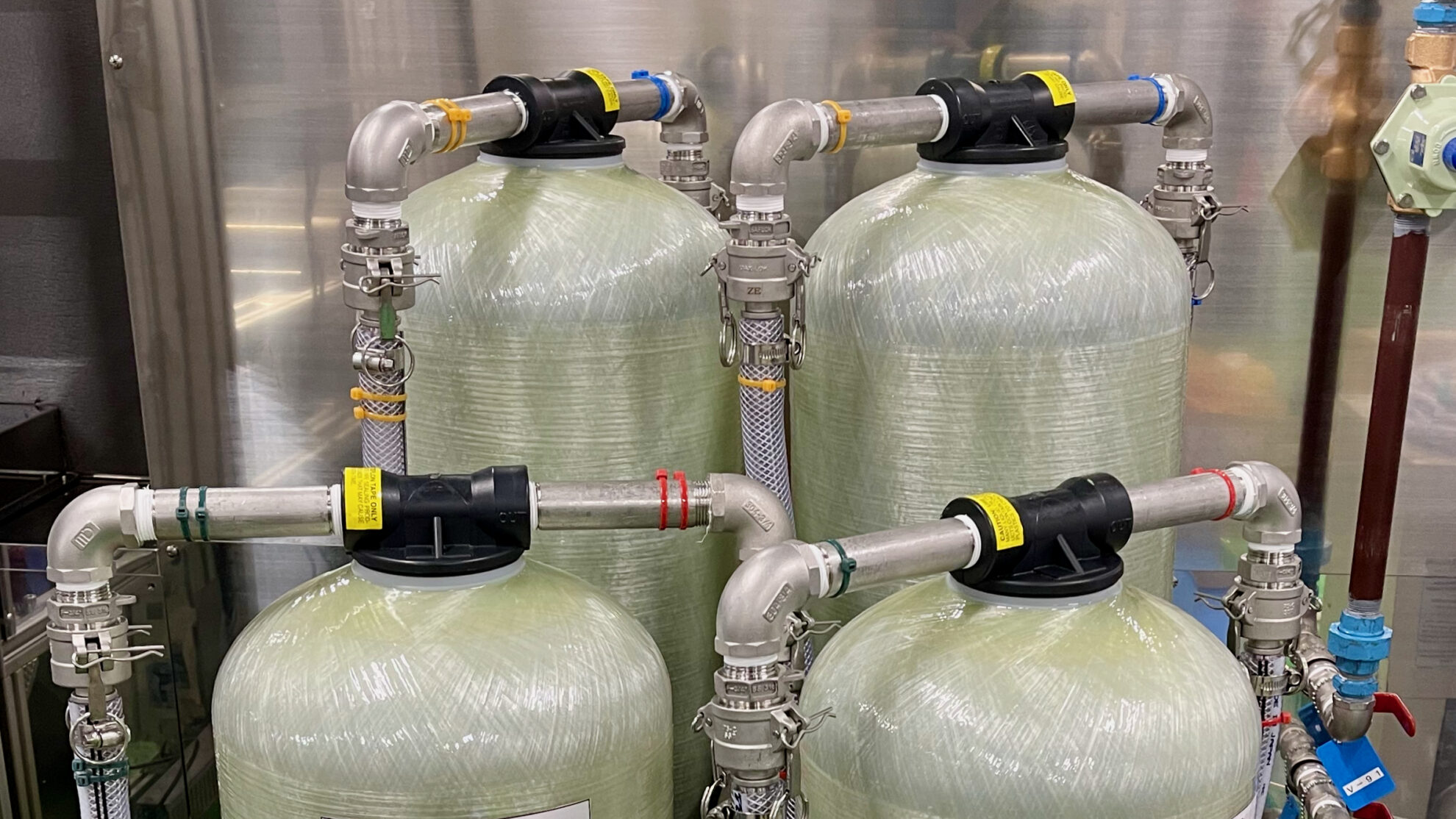
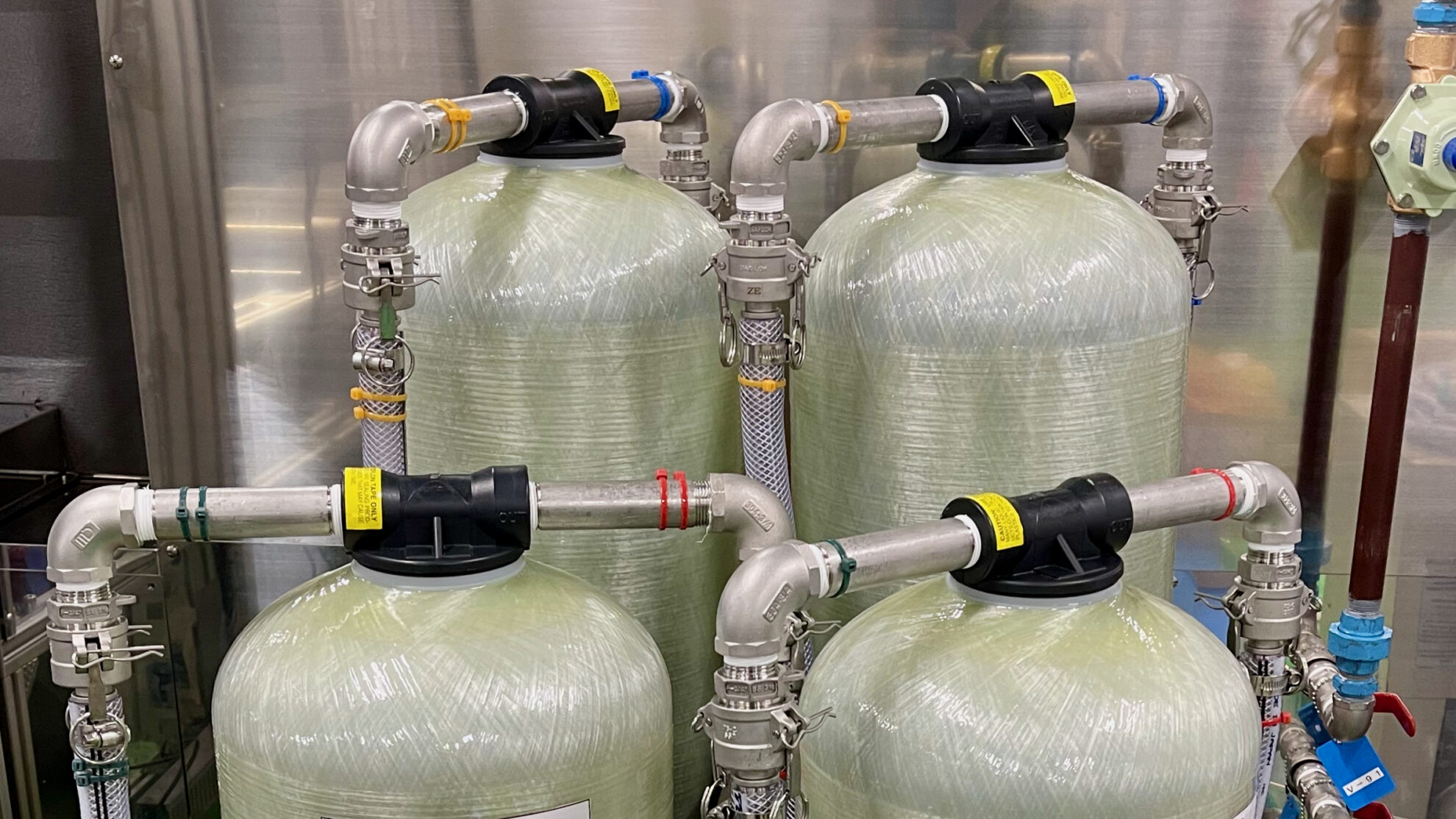
Ancillary equipment can be incorporated into the process, including water treatment such as pure water or ion-exchanged water production, solvent recovery such as distillation and regeneration, concentration, filtration, sterilization, etc.
Conveyor system
We determine the most suitable conveyor system for actual precision cleaning processes from among net conveyors, basket conveyors, hoop conveyors, etc. We use our own algorithms to adopt controls that can shorten the operation time.
Piping system
We design necessary liquid piping and process gas piping systems based on the overall process configuration. Piping systems include supply, discharge, recovery, circulation, etc. Each system includes valves, filters, pumps, etc.
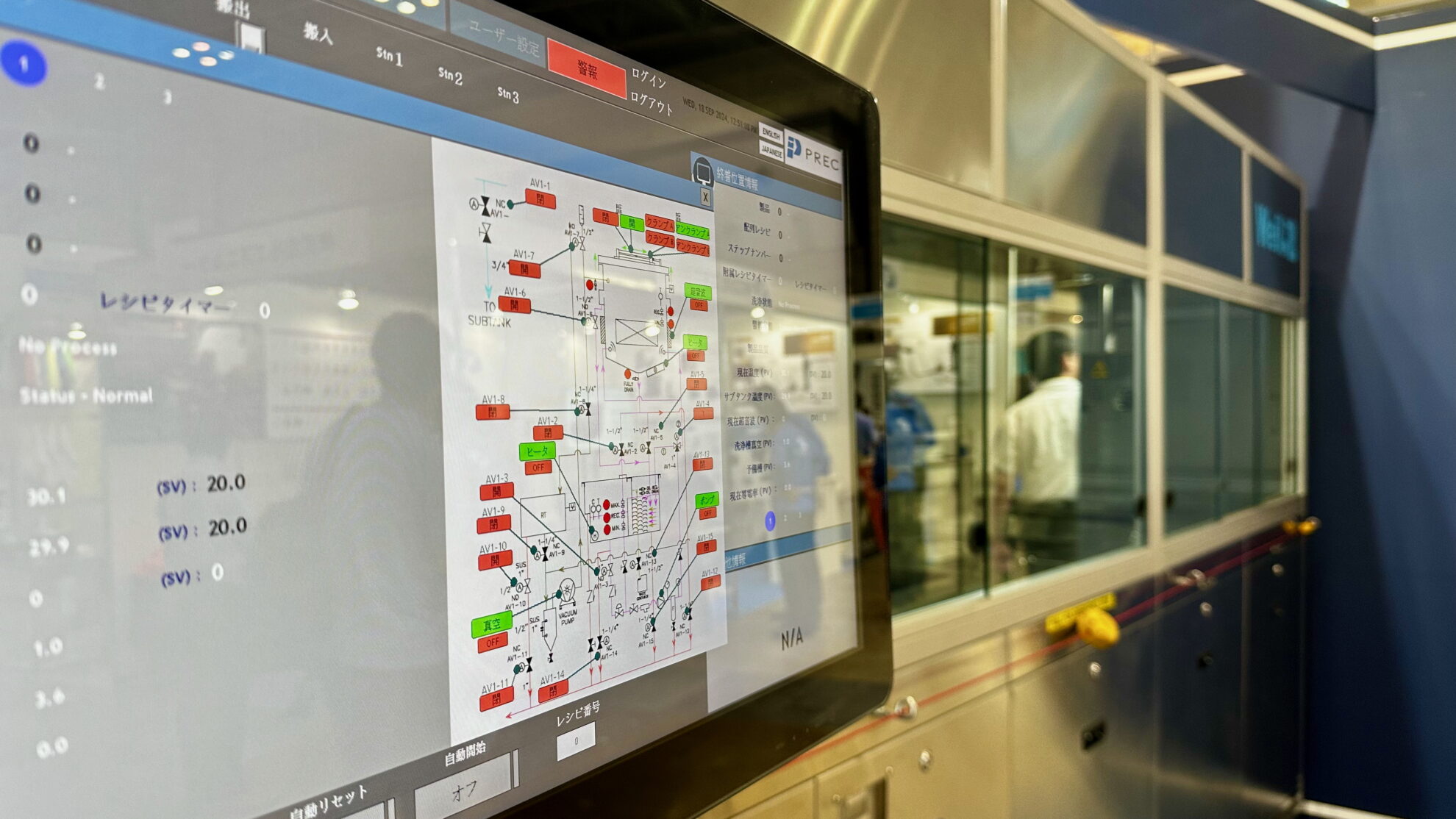
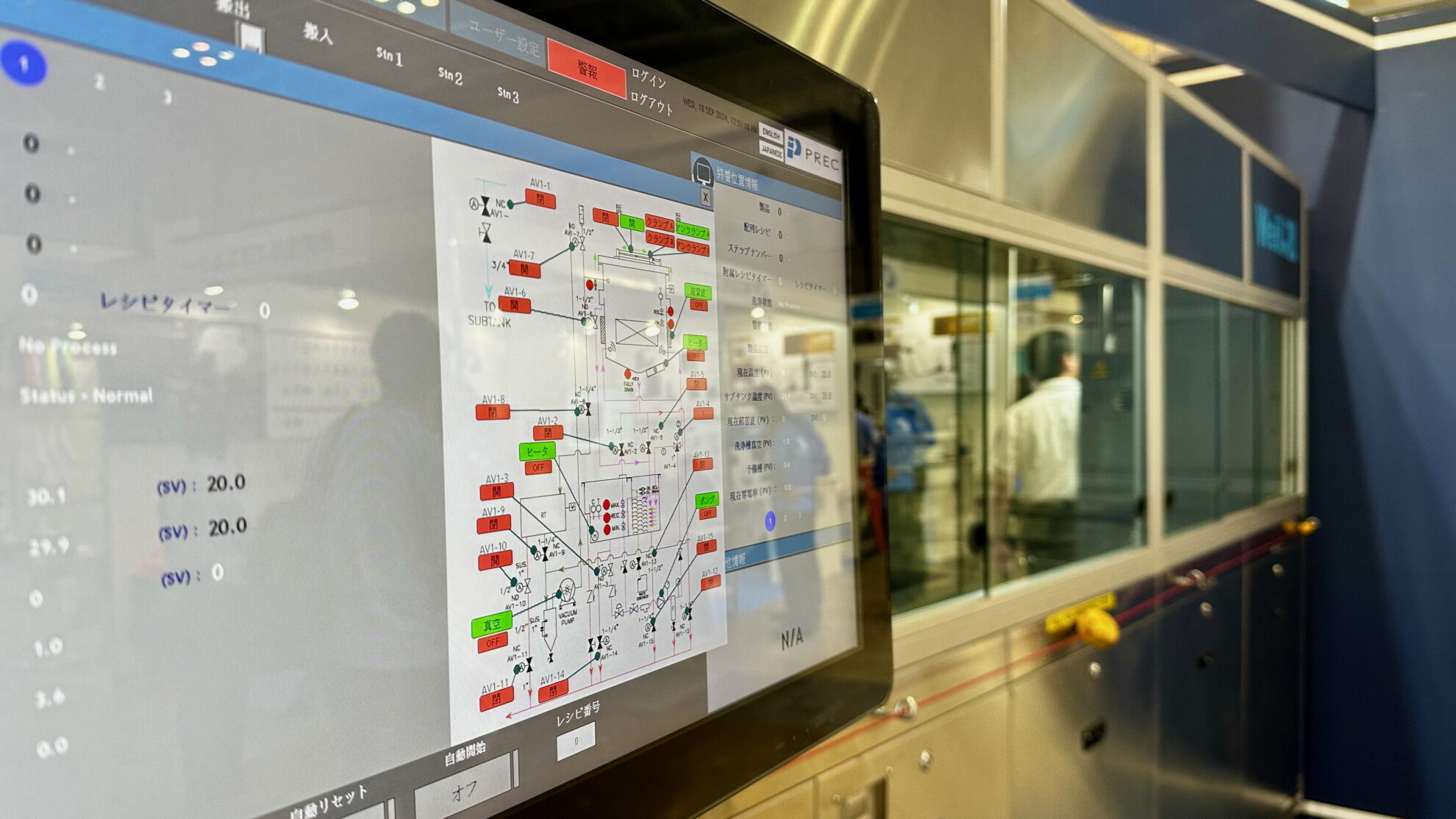
Process control
To control the entire process, various sensors are used to monitor liquid temperature, concentration, level, etc., and liquid and gas flow rates and pressures are also controlled. Conveyor system controls, automation sequences, data logging, etc. can also be integrated in the system.
Utilities
Utilities consist of electricity, dry compressed air, steam, etc.
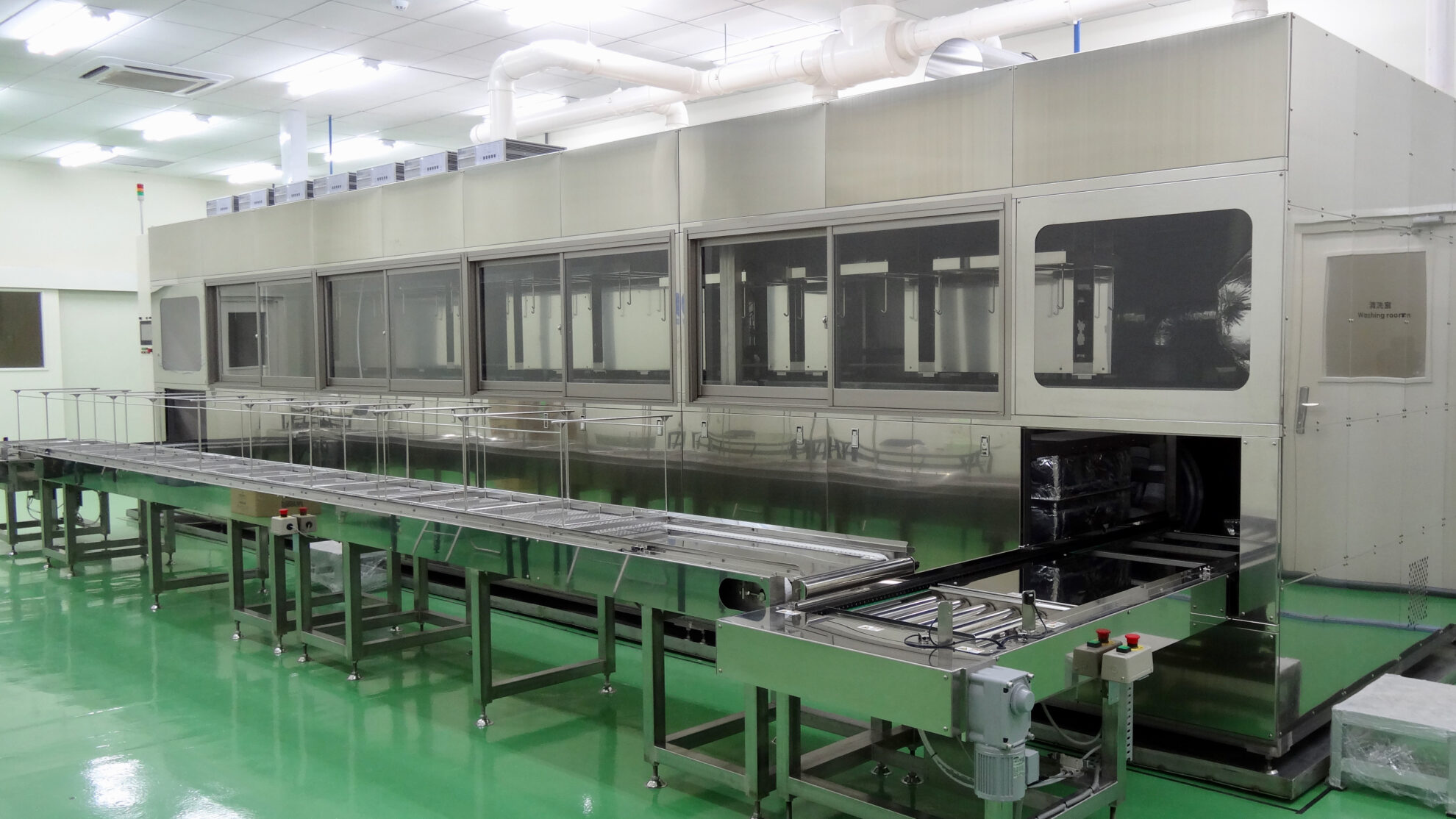
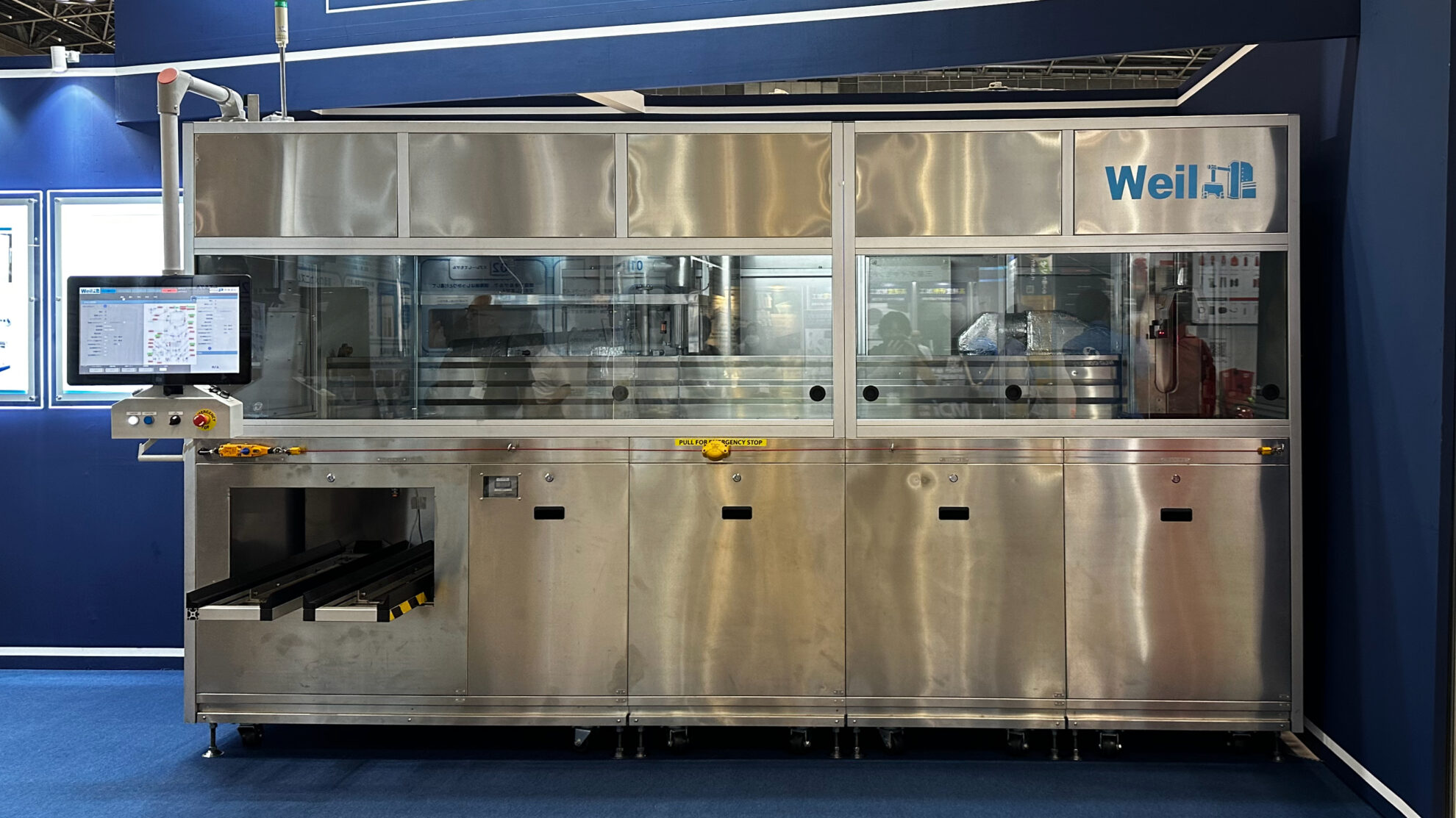
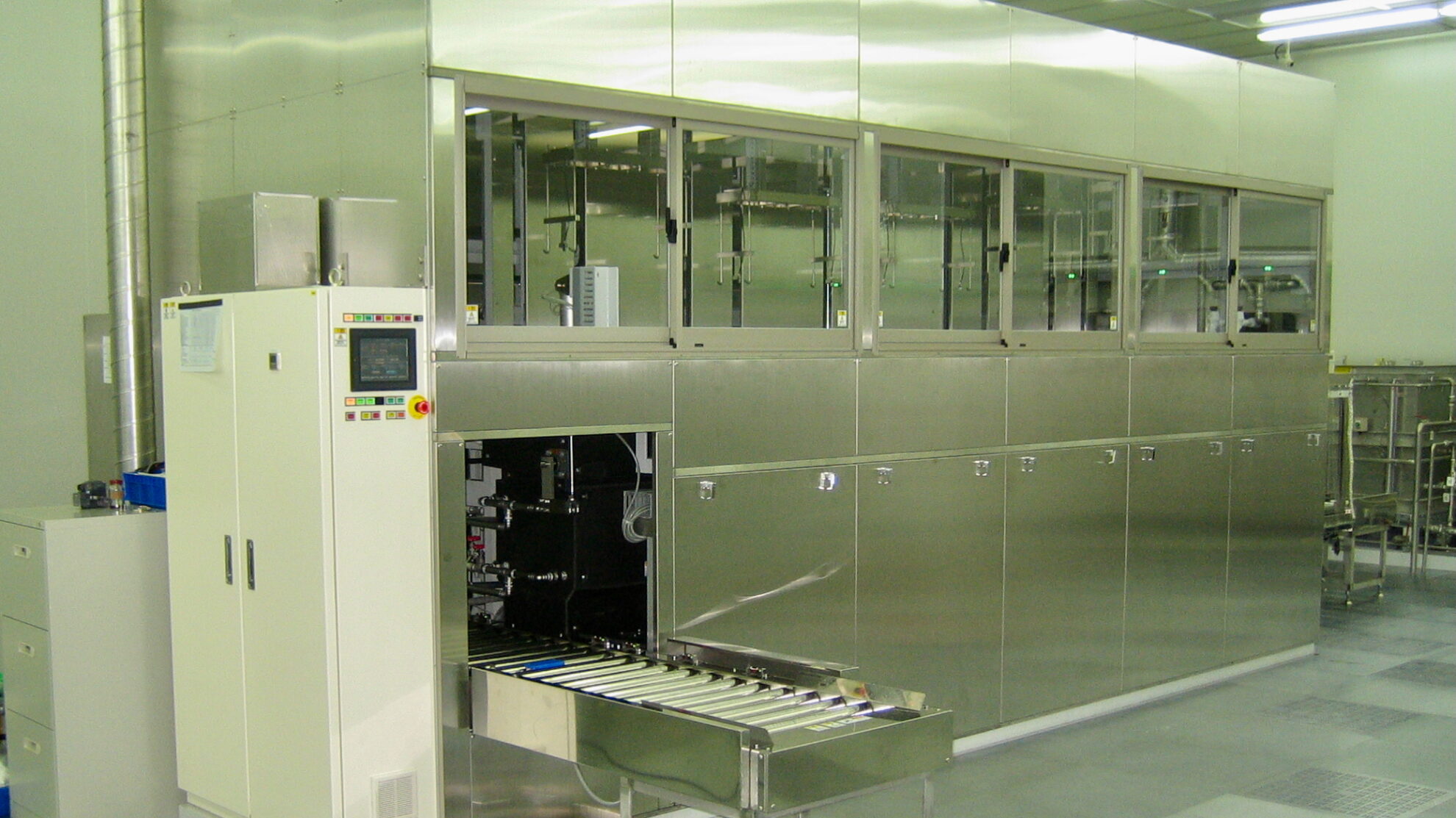
We provide precision cleaning processes that combine high cleaning performance with environmental friendliness. We handle a wide range of cleaning methods, including ultrasonic, spray, shower, submerged jet, barrel, degassing, vacuum, and combinations of these methods. We design processes that minimize the consumption of cleaning chemicals and operating costs, such as electricity consumption. Ancillary equipment includes dehydration, vacuum drying, vapor drying, concentration, filtration, distillation regeneration, pure water production and regeneration, etc., depending on the applications. Conveyor systems can be selected from among net conveyor, basket, hoop, etc. Cleaning processes can be controlled from manual to full automation. It is also possible to implement the minimum level of automation according to the budget constraints. Recipe and lot management, communication between pre- and post-processes, and communication with the user’s central control system can also be supported.
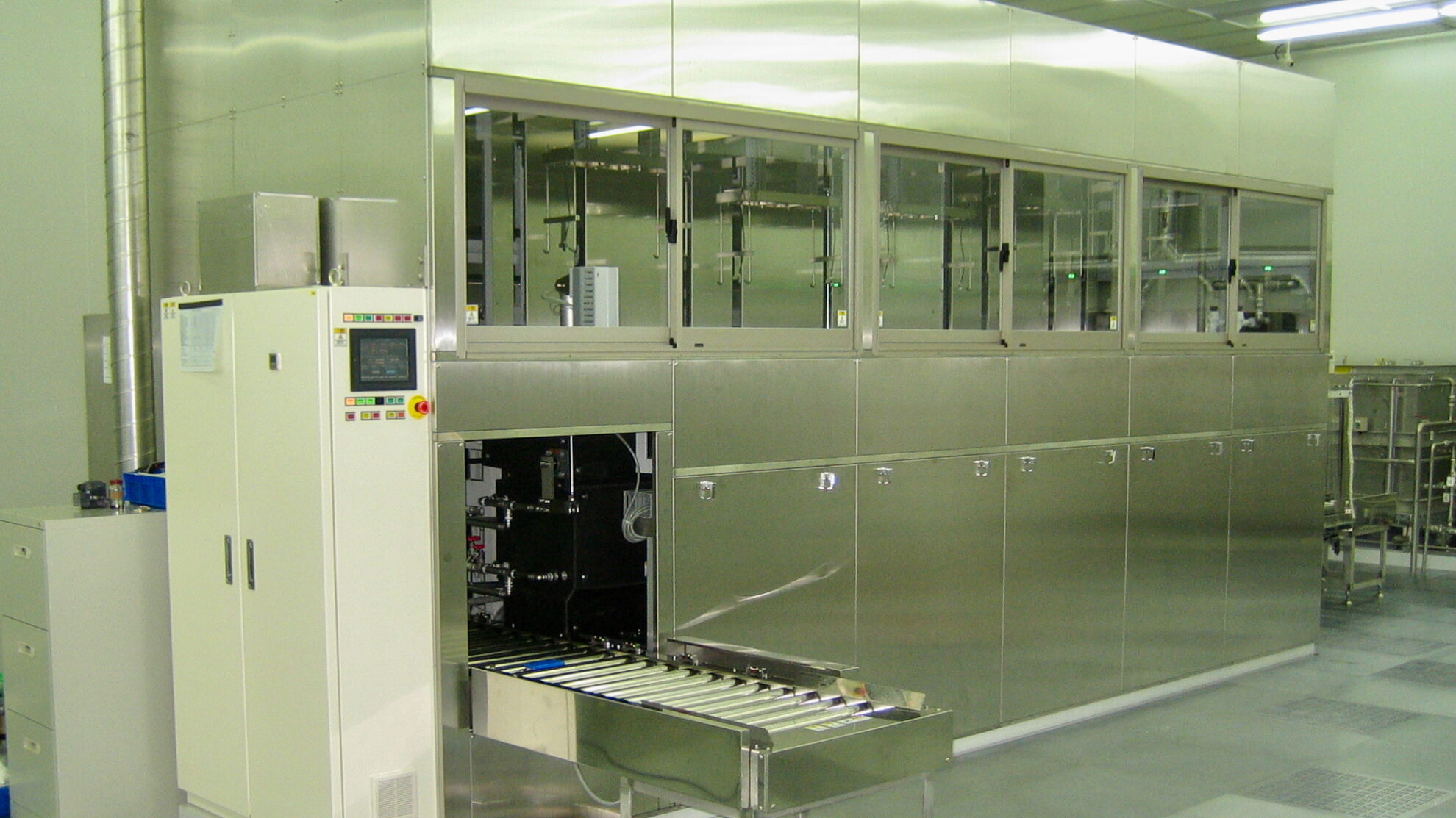
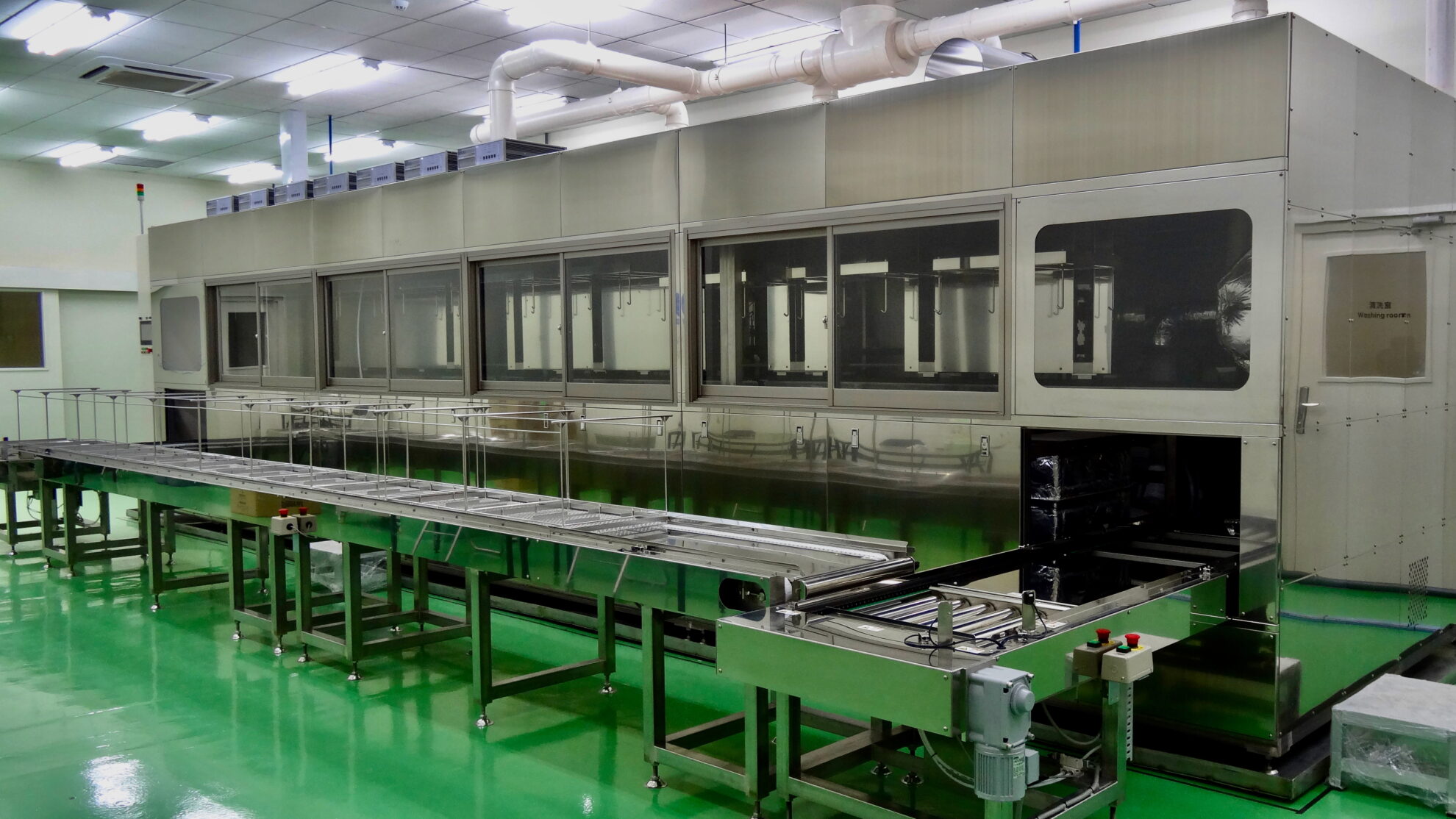

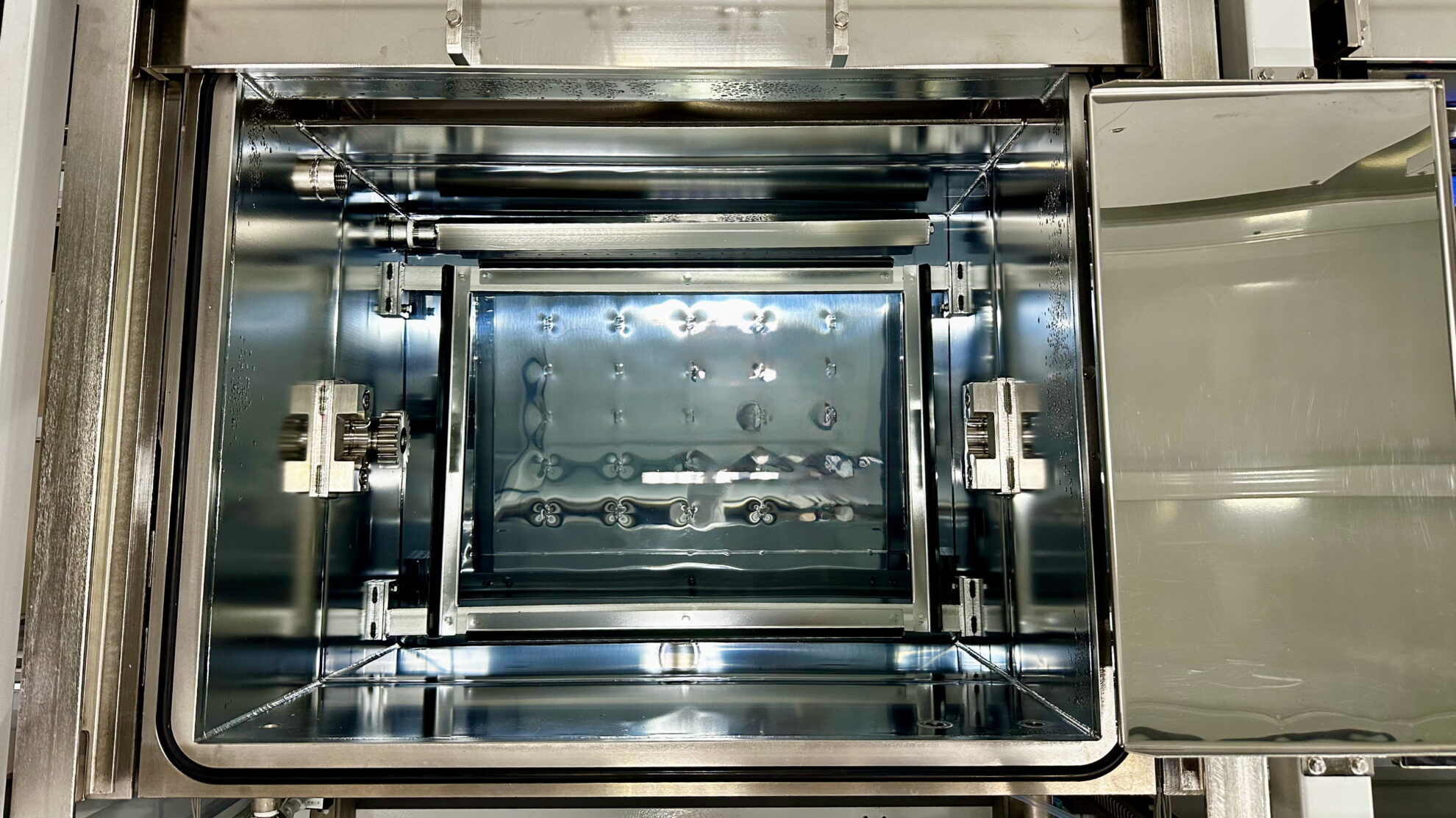

Our cleaning test center (CTC) offers cleaning trials using actual workpieces, as well as analysis and measurement services. Through partnerships with a wide variety of cleaning chemical suppliers, we rationally determine and propose the most cost-effective chemicals in terms of performance.